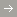TOWING REQUIREMENTS
The 787-8 shares a common towbar nose tow fitting with the 767 and 777. As with Boeing airplanes, the 787-8 towbar has a unique shear pin. Boeing towbar specification drawing K09001 provides data on towing loads, which can be accessed through the Web portal MyBoeingFleet.com.
The 787-8 can use the same tow tractor as the 777. With a maximum taxi weight of 486,000 pounds (220,446 kilograms), the tow tractor should have a design weight of 75,600 pounds (34,291 kilograms) and a drawbar pull of 34,020 pounds (15,431 kilograms). The coefficient of friction between the tractor tire and pavement used is 0.45. The 787-8 is also compatible with towbarless vehicles. As with the 777, the amount that a towbarless vehicle is used for dispatching a 787-8 for flight is limited to 25 percent. The Service Letter 787-SL-09-001 contains details on towbarless towing and has been updated to include the 787.
ELECTRICAL POWER
The 787-8 airplane utilizes two forward ground power receptacles and one mid-aft ground power receptacle. Receptacle ground heights are minimum 81 inches (206 centimeters) and maximum 108 inches (274 centimeters). Each receptacle is rated at 90 kilovolt amperes (KVA), the same as other Boeing twin-aisle production airplanes.
Similar to existing airplanes, the 787 utilizes power from the auxiliary power unit (APU) for engine start. The 787 is different in that it uses electrical power for engine start rather than the pneumatic power used on existing airplanes. If the APU is inoperative, an engine start can be performed using a minimum of two 90 KVA external ground power units (GPUs). Boeing recommends the use of three 90 KVA ground power sources to decrease engine start times and minimize ramp impact during ground operations. Same as the 777 and other twin-aisle airplanes, the ground power requirements must conform to the electrical power quality requirements specified in figure 5.
Ground Power Requirements
Figure 5
| PARAMETER | 787 GROUND POWER EQUIPMENT REQUIREMENTS (EXTERNAL POWER BUS PROTECTION) | |
| Power consumption | Maximum power consumption (per receptacle) | 90 kilovolt amperes (KVA) (continuous) |
| Peak power consumption (per receptacle) | 112.5 KVA, 0.75–1.0 pico-farad per receptacle (5 minutes) | |
| Voltage requirements | Normal voltage range | 115/200 + /– 2 volts alternating current (VAC) |
| Allowable voltage range | 115 + /– 5 VAC L–N root mean square (RMS) | |
| Frequency requirements | Normal frequency | 400 + /– 5 Hertz (Hz) |
| Allowable frequency range | 400 +18 /–15 Hz | |
| Maximum Distortion Factor | Total harmonic content | 3% of fundamental |
| Individual harmonic content | 2% of fundamental | |
| Crest factor | 1.414 + /– 0.07 | |
| Maximum voltage modulation factor | 2.5 V peak to valley (0.5%) | |
| External power bus protection (on airplane) | 115 V bus, overvoltage | Above 182 VRMS (2.5 + /– .5 second [sec]) = “trip”
132 VRMS – 129 VRMS (2.5 + /– 0.25 sec) = “may trip” |
| 115 V bus, undervoltage | Below 103 VRMS (0.5 + /– 0.25 sec) = “trip”
103 VRMS – 106 VRMS (0.5 + /– 0.25 sec) = “may trip” * Undervoltage trip inhibited during fault conditions when over current is present |
|
| Overfrequency | Above 430 Hz (1.0 + /– 0.2 sec) = “trip”
425 Hz – 430 Hz (1.0 + /– 0.2 sec) = “may trip” |
|
| Underfrequency | Below 370 Hz (1.0 + /– 0.2 sec) = “trip”
370 Hz – 375 Hz (1.0 + /– 0.2 sec) = “may trip” |